Adding file-sources to Galaxy
Under Development!
This tutorial is not in its final state. The content may change a lot in the next months. Because of this status, it is also not listed in the topic pages.
| Author(s) |
|
| Reviewers |
|
OverviewQuestions:
Objectives:
How to set up an S3 bucket
Add your S3 bucket on Galaxy
Time estimation: 15 minutesSupporting Materials:
Published: Jan 20, 2025Last modification: Jan 20, 2025License: Tutorial Content is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The GTN Framework is licensed under MITpurl PURL: https://gxy.io/GTN:T00529version Revision: 1
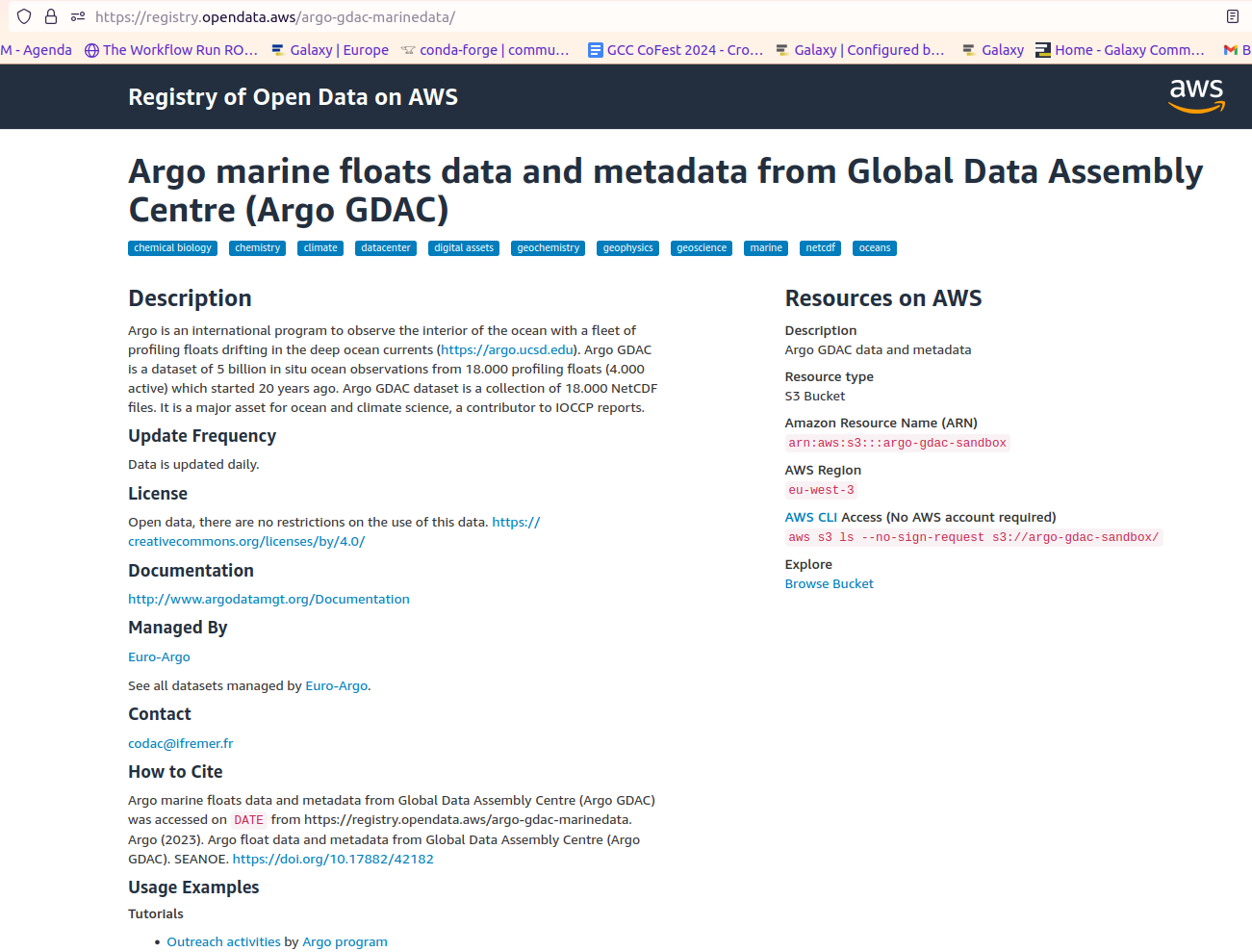
This tutorial demonstrates how to implement an S3 bucket as a Galaxy file-source within Galaxy. We will add here the public Argo data Amazon S3 bucket. Argo is an international program that observes the interior of the ocean with a fleet of profiling floats drifting in the deep ocean currents (https://argo.ucsd.edu). It started 20 years ago and is a dataset of 5 billion in situ ocean observations from 18.000 profiling floats (4.000 active). The Argo GDAC dataset is a collection of 18.000 NetCDF files. It is a major asset for ocean and climate science and a contributor to IOCCP reports.
AgendaIn this tutorial, we will cover:
Find the information you need
Hands On: Find an S3 bucketGo on Amazon Sustainability Data Initiative.
There you can visit the catalog of data, and by searching for Argo you can directly get to the Argo registry.
On this last page you’ll find all the information you’ll need to add the S3 bucket to Galaxy
Add the S3 bucket
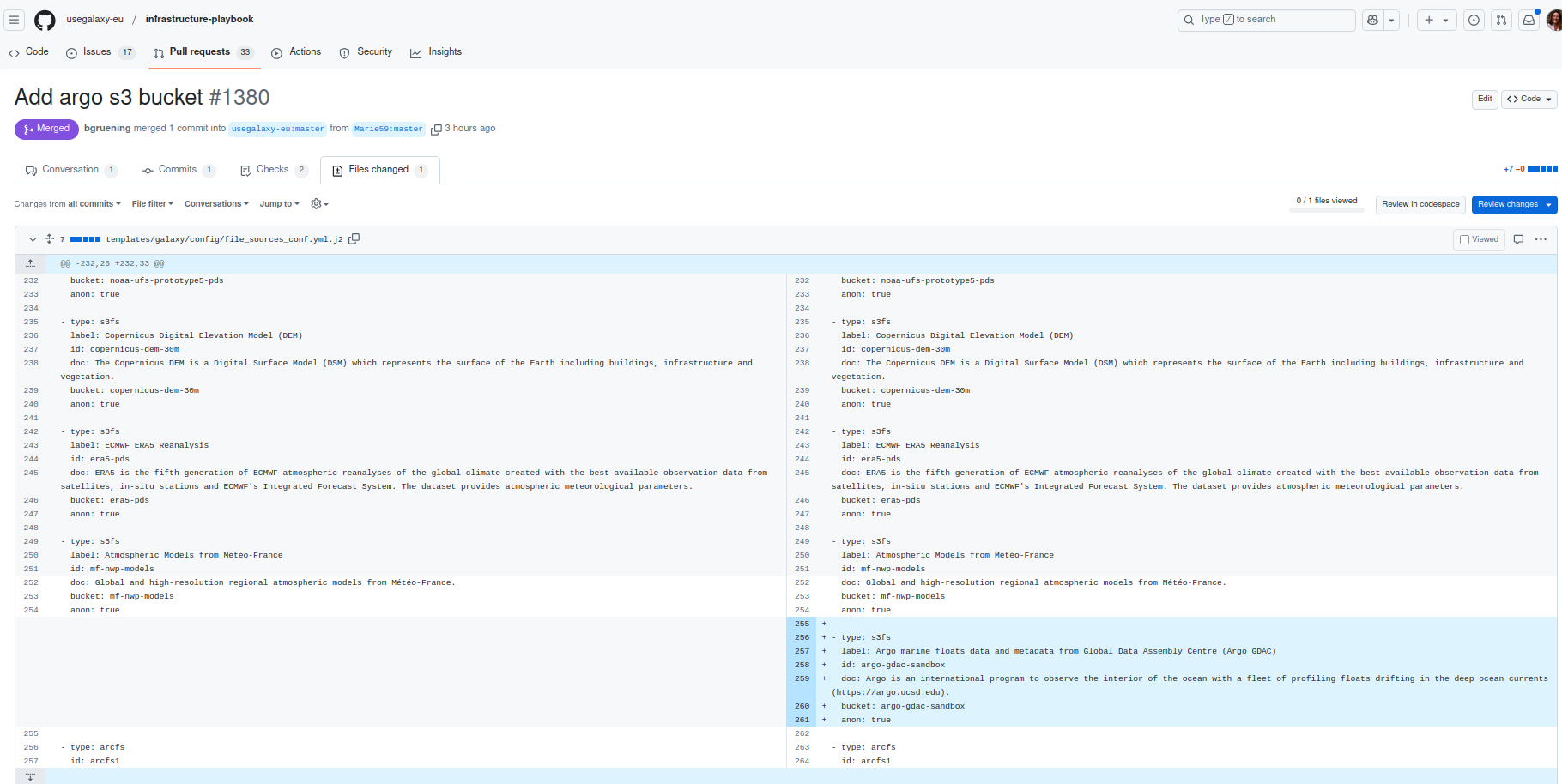
Hands On: Add on Galaxy
- If not already done clone the Galaxy Europe Infrastructure-playbook repo
- Create a branch on your fork
- Go to the file file_sources_conf.yml.j2 in templates/galaxy/config/
There you can edit the file and add your S3 bucket by adding a Argo specific section, like in the following:
- type: s3fs label: Argo marine floats data and metadata from Global Data Assembly Centre (Argo GDAC) id: argo-gdac-sandbox doc: Argo is an international program to observe the interior of the ocean with a fleet of profiling floats drifting in the deep ocean currents (https://argo.ucsd.edu). bucket: argo-gdac-sandbox anon: trueFinally, commit your changes and write a nice message for the admin when you open your Pull Request.
Conclusion
Here you are all set and once your Pull Request is merged you’ll soon be able to see your bucket in upload data, Choose remote files, and then search for your bucket label !