name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse <div class="my-header"><span> <a href="/training-material/topics/evolution" title="Return to topic page" ><i class="fa fa-level-up" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> <a href="https://github.com/galaxyproject/training-material/edit/main/topics/evolution/tutorials/abc_intro_phylo-networks/slides.html"><i class="fa fa-pencil" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> </span></div> <div class="my-footer"><span> <img src="/training-material/shared/images/biocommons-utas.png" alt="page logo" style="height: 40px;"/> </span></div> --- <img src="/training-material/shared/images/biocommons-utas.png" alt="page logo" class="cover-logo" /> <br/> <br/> # Phylogenetics - Back to Basics - Phylogenetic Networks <br/> <br/> <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> <ul class="text-list"> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/mcharleston/" class="contributor-badge contributor-mcharleston"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/mcharleston?s=36" alt="Michael Charleston avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Michael Charleston</a></li> </ul> </div> </div> <!-- modified date --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 8em;"> <i class="far fa-calendar" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">last_modification</span> Updated: <i class="fas fa-fingerprint" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">purl</span><abbr title="Persistent URL">PURL</abbr>: <a href="https://gxy.io/GTN:S00119">gxy.io/GTN:S00119</a> </div> <!-- other slide formats (video and plain-text) --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 5em;"> <i class="fas fa-file-alt" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">text-document</span><a href="slides-plain.html"> Plain-text slides</a> | </div> <!-- usage tips --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 2em;"> <strong>Tip: </strong>press <kbd>P</kbd> to view the presenter notes | <i class="fa fa-arrows" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">arrow-keys</span> Use arrow keys to move between slides </div> ??? Presenter notes contain extra information which might be useful if you intend to use these slides for teaching. Press `P` again to switch presenter notes off Press `C` to create a new window where the same presentation will be displayed. This window is linked to the main window. Changing slides on one will cause the slide to change on the other. Useful when presenting. --- ## Requirements Before diving into this slide deck, we recommend you to have a look at: - [Introduction to Galaxy Analyses](/training-material/topics/introduction) --- #About these slides <br> <br> The following phylogenetic networks of _Anolis_ species were generated in SplitsTree. They represent selected screenshots of networks explored as a live demo in the video associated with these slides. --- #Uncorrected P model <br> Phylogenetic network of _Anolis_ species created in SplitsTree using the uncorrected P model.  --- #Exploring splits <br> Click on the branches of the network to explore different splits. Here _A. ahli_ appears in two different splits highlighted in yellow. .pull-left[  ] .pull-right[  ] --- #Let's follow a split <br> This is the network made using the uncorrected p model. We will follow the split containing _A. lineatopus_ and _A. limifrons_ through different models.  --- #Jukes Cantor Model <br> These networks were created using the Jukes Cantor model. Note that the species _A. limifrons_ appears in two alternate splits. .pull-left[  ] .pull-right[ 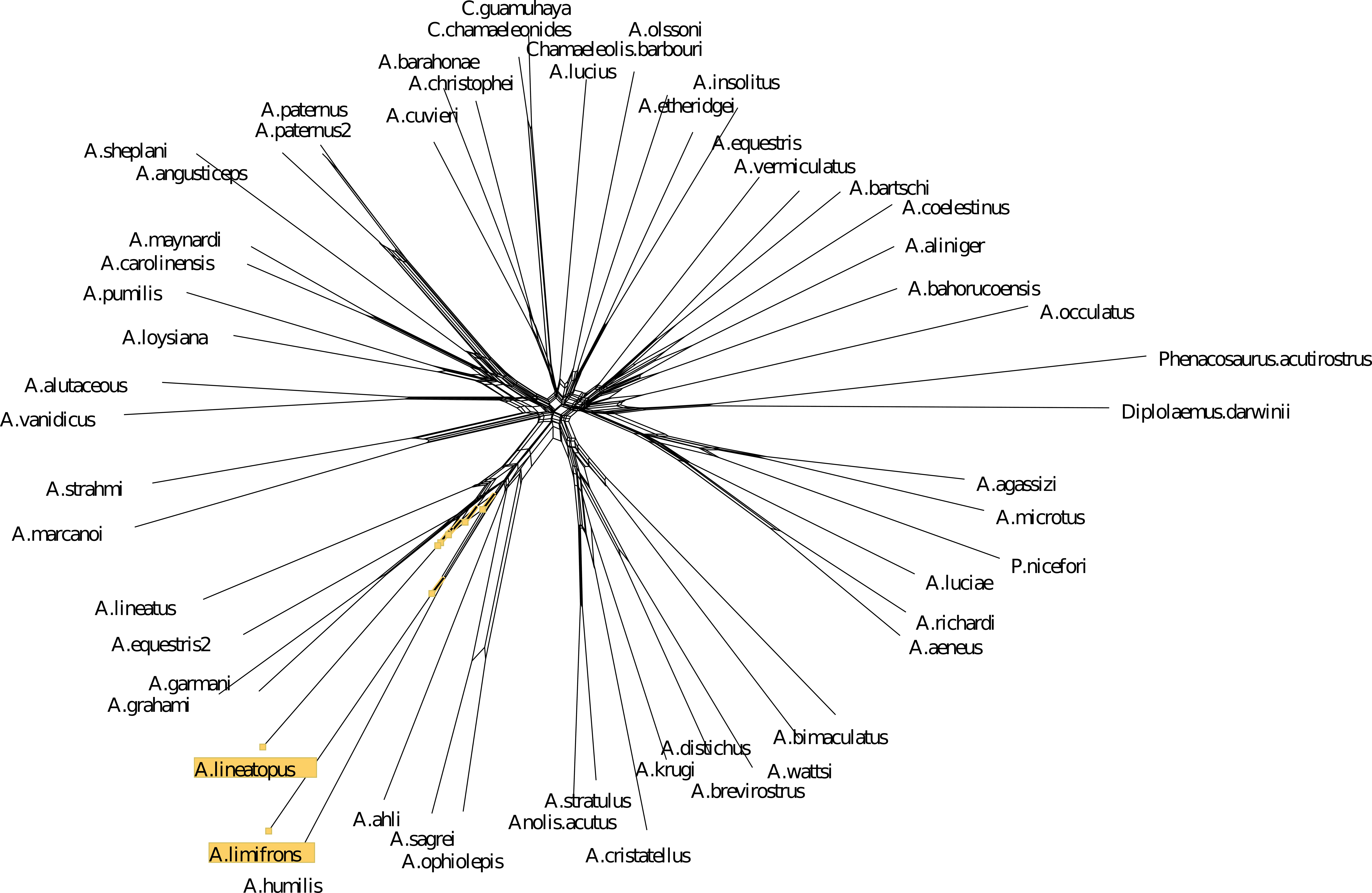 ] --- #HKY85 Model <br> This network was created with the HKY85 model. Note that _A. limfrons_ is paired with _A. humilis_ in this split.  --- #Bootstrapped network <br> 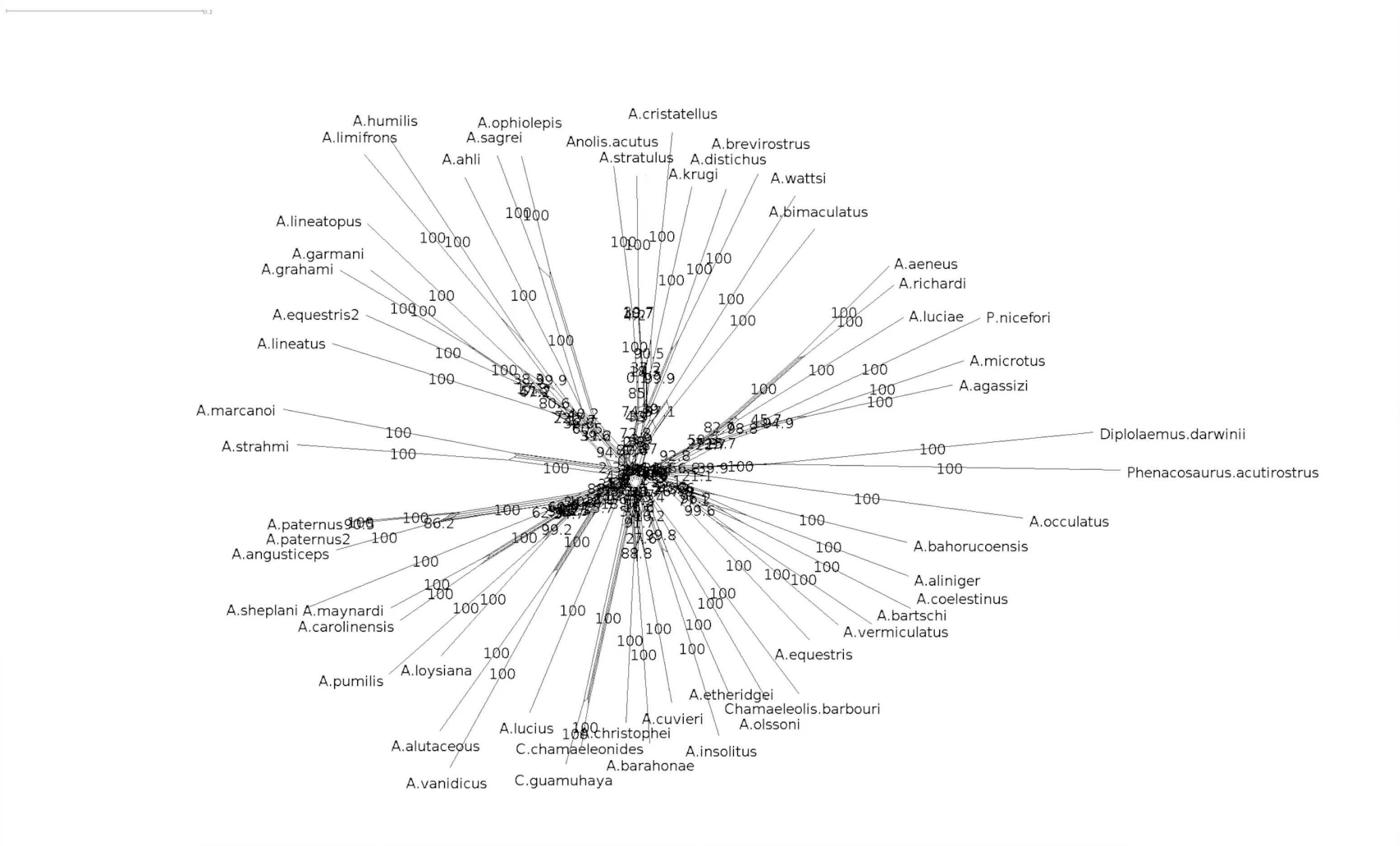 --- #Bootstrapped network - a closer look <br> Let's explore our two splits again .pull-left[ 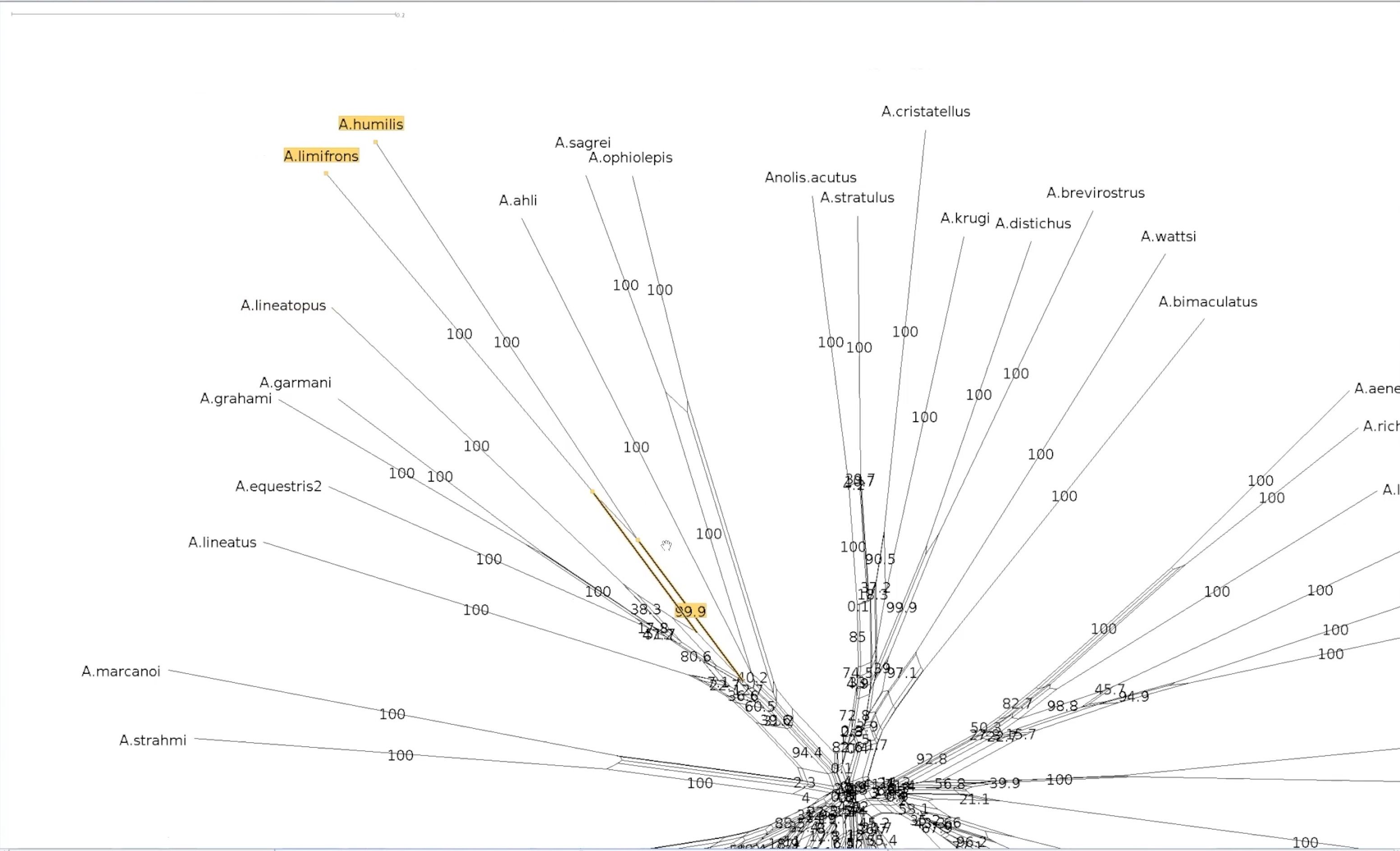 ] .pull-right[ 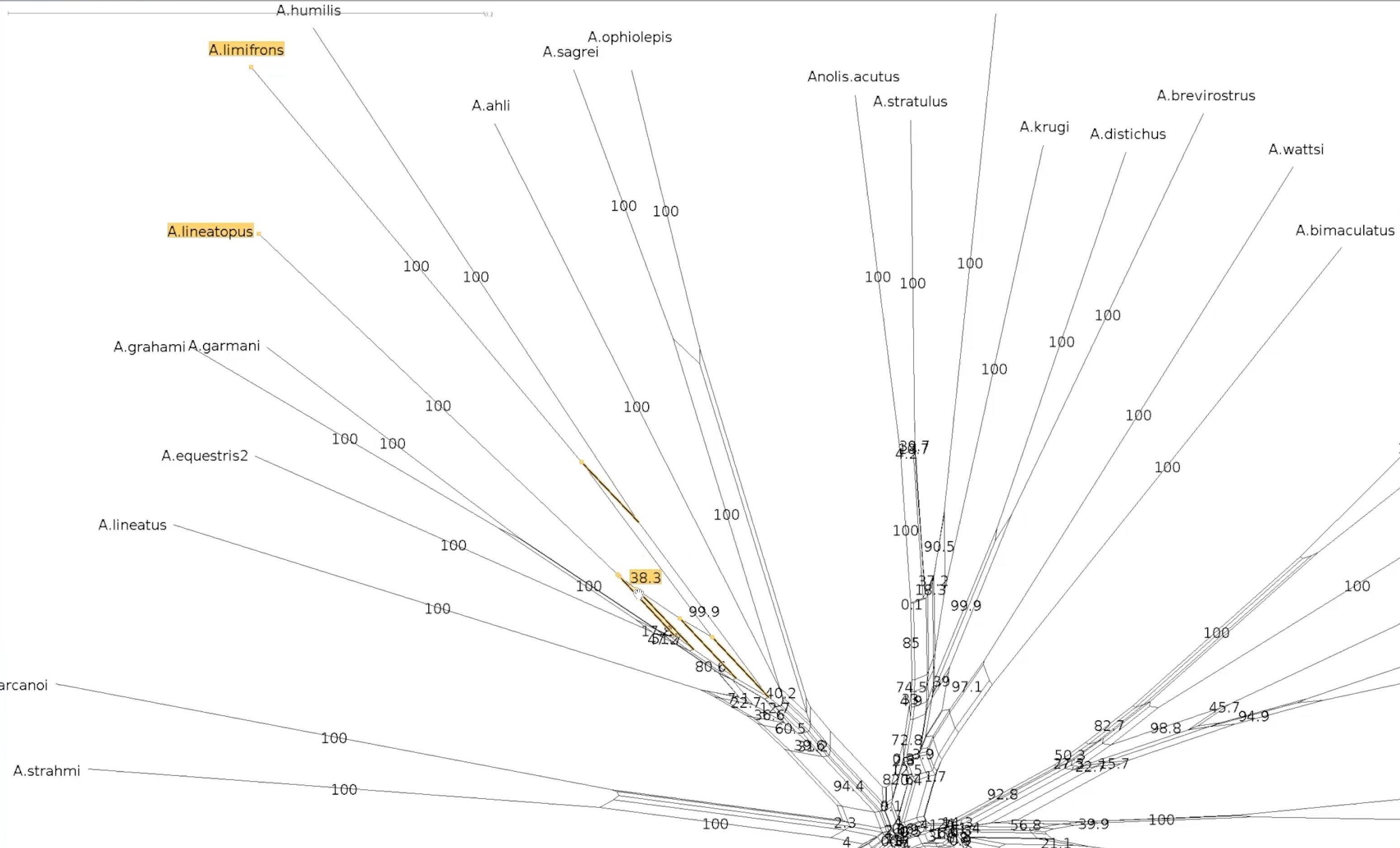 ] --- #Bootstrapped network - a closer look <br> This the centre of our bootstrapped network. Note that the values are smaller. 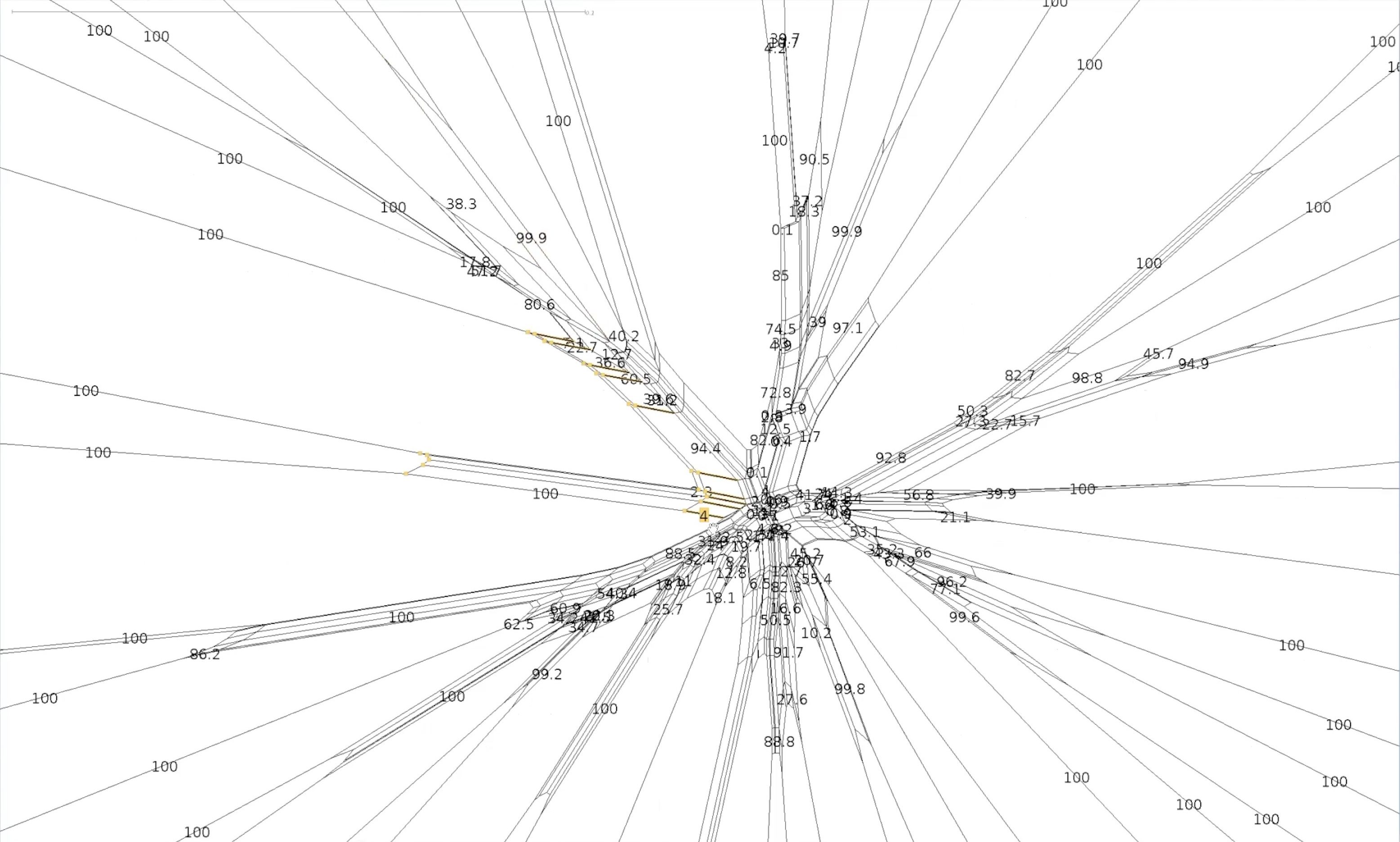 --- # Thank you! --- --- ## Thank You! This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the [Galaxy Training Network](https://training.galaxyproject.org) and all the contributors! <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> <table class="contributions"> <tr> <td><abbr title="These people wrote the bulk of the tutorial, they may have done the analysis, built the workflow, and wrote the text themselves.">Author(s)</abbr></td> <td> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/mcharleston/" class="contributor-badge contributor-mcharleston"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/mcharleston?s=36" alt="Michael Charleston avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Michael Charleston</a> </td> </tr> <tr class="reviewers"> <td><abbr title="These people reviewed this material for accuracy and correctness">Reviewers</abbr></td> <td> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/hexylena/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-hexylena"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/hexylena?s=36" alt="Helena Rasche avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/burkemlou/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-burkemlou"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/burkemlou?s=36" alt="Melissa Burke avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/shiltemann/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-shiltemann"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/shiltemann?s=36" alt="Saskia Hiltemann avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a></td> </tr> </table> </div> </div> <div style="display: flex;flex-direction: row;align-items: center;justify-content: center;"> <img src="/training-material/shared/images/biocommons-utas.png" alt="page logo" style="height: 100px;"/> </div> Tutorial Content is licensed under <a rel="license" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/">Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License</a>.<br/>