| Author(s) |
|
Posted on: 30 June 2021 purlPURL: https://gxy.io/GTN:N00019
Effectively monitoring global infectious disease crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, requires capacity to generate and analyze large volumes of sequencing data in near real time. These data have proven essential for monitoring the emergence and spread of new variants, and for understanding the evolutionary dynamics of the virus.
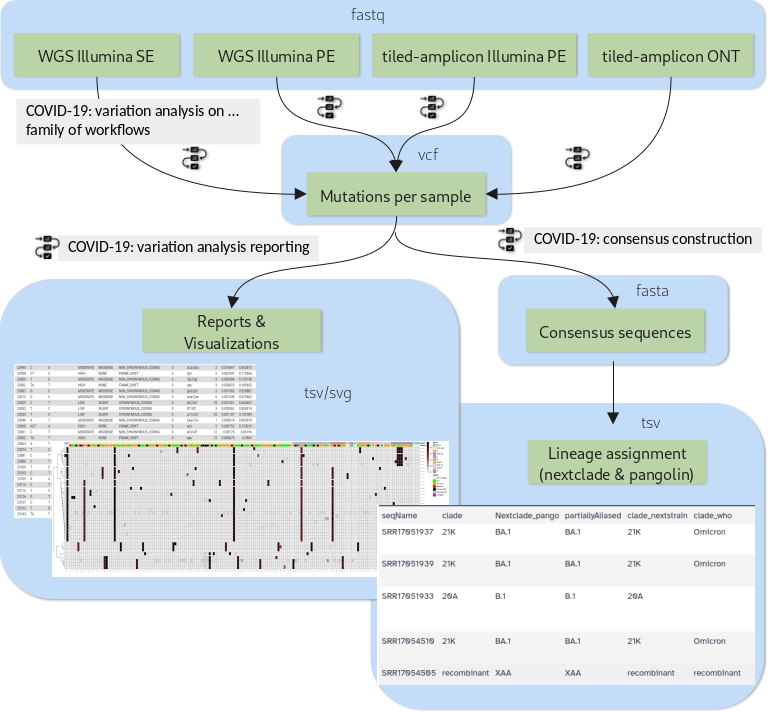
The Galaxy community has developed high-quality analysis workflows to support
- sensitive identification of SARS-CoV-2 allelic variants (AVs) starting with allele frequencies as low as 5% from deep sequencing reads
- generation of user-friendly reports for batches of results
- reliable and configurable consensus genome generation from called variants
The new tutorial “Mutation calling, viral genome reconstruction and lineage/clade assignment from SARS-CoV-2 sequencing data” will teach you how to obtain, run and combine these workflows appropriately for different types of input data, be it:
- Single-end data derived from Illumina-based RNAseq experiments
- Paired-end data derived from Illumina-based RNAseq experiments
- Paired-end data generated with Illumina-based Ampliconic (ARTIC) protocols, or
- ONT FASTQ files generated with Oxford nanopore (ONT)-based Ampliconic (ARTIC) protocols
We would be happy to have your feedback or contributions for this new tutorial. That would help us improving it!
View Material