Frequently Asked Questions
Tutorial Questions
Can EncyclopeDIA be run on a DIA-MS dataset without a spectral library?
Question: Can EncyclopeDIA be run on a DIA-MS dataset without a spectral library?Yes. In this GTN, the workflow presented is the Standard EncyclopeDIA workflow; however, there is a variation upon the Standard EncyclopeDIA workflow, named the WALNUT EncyclopeDIA workflow in which a spectral library is not required. Simply, the WALNUT variation of the workflow omits the DLIB spectral/PROSIT library input, hence requiring just the GPF DIA dataset collection, Experimental DIA dataset collection, and the FASTA Protein Database file. Therefore, the Chromatogram Library is generated using the GPF DIA dataset collection and the FASTA Protein Database alone. This method does generate fewer searches than if a spectral library is used. The Galaxy-P team tested the efficacy of the WALNUT workflow compared to the Standard EncyclopeDIA workflow, and more information on that comparison and those results can be found at this link.
What advantages does a Chromatogram Library have over a DDA-generated library or predicted spectral library?
Question: What advantages does a Chromatogram Library have over a DDA-generated library or predicted spectral library?While generating a Chromatogram Library is the most time consuming step of the EncyclopeDIA workflow, it is beneficial to DIA data analysis. DIA is a novel technique and methods for DIA data analysis are still being developed. One method commonly used includes searching DIA data against DDA-generated libraries. However, there are limitations in this method. Firstly, DDA-generated libraries are not always an accurate representation of DIA data: differences in the methods of data collection play an important role in the efficacy of the library. Secondly, DDA-generated libraries often require labs to run completely separate DDA experiments to simply generate a library with which to analyze their DIA data. Chromatogram Libraries mitigate some of the previous shortcomings mentioned. DIA data is incorporated into the generation of the Chromatogram Library and therefore provides context to the DIA data being analyzed. Secondly, the ELIB format of the Chromatogram Library allows for extra data to be included in the analysis of the DIA data, including intensity, m/z ratio, and retention time compared to the use of a DDA-generated DLIB library. Lastly, a Chromatogram Library can be generated without the use of a spectral library (as mentioned in the last question). Therefore, it is possible to forgo DDA data collection as the DLIB DDA-generated library is not strictly needed for Chromatogram Library generation and to run the EncyclopeDIA workflow (saving time and resources).
General Questions
Can't find one of the tools for this tutorial?
To use the tools installed and available on the Galaxy server:
- At the top of the left tool panel, type in a tool name or datatype into the tool search box.
- Shorter keywords find more choices.
- Tools can also be directly browsed by category in the tool panel.
If you can’t find a tool you need for a tutorial on Galaxy, please:
- Check that you are using a compatible Galaxy server
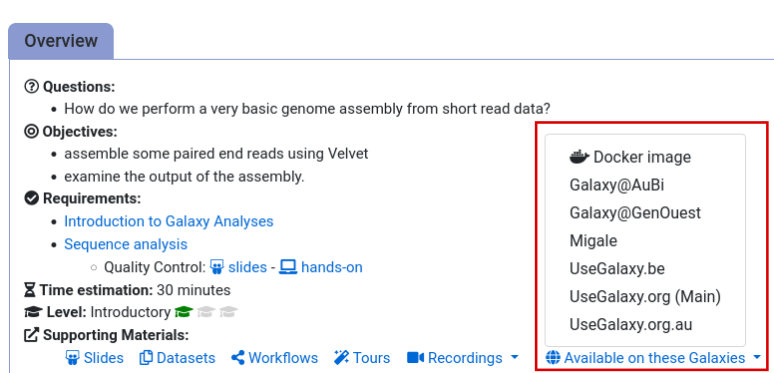
- Navigate to the overview box at the top of the tutorial
- Find the “Supporting Materials” section
- Check “Available on these Galaxies”
- If your server is not listed here, the tutorial is not supported on your Galaxy server
- You can create an account on one of the supporting Galaxies
- Use the Tutorial mode feature
- Open your Galaxy server
- Click on the curriculum icon on the top menu, this will open the GTN inside Galaxy.
- Navigate to your tutorial
- Tool names in tutorials will be blue buttons that open the correct tool for you
- Note: this does not work for all tutorials (yet)
- Still not finding the tool?
- Ask help in Gitter.
Running into an error?
When something goes wrong in Galaxy, there are a number of things you can do to find out what it was. Error messages can help you figure out whether it was a problem with one of the settings of the tool, or with the input data, or maybe there is a bug in the tool itself and the problem should be reported. Below are the steps you can follow to troubleshoot your Galaxy errors.
- Expand the red history dataset by clicking on it.
- Sometimes you can already see an error message here
View the error message by clicking on the bug icon galaxy-bug
- Check the logs. Output (stdout) and error logs (stderr) of the tool are available:
- Expand the history item
- Click on the details icon
- Scroll down to the Job Information section to view the 2 logs:
- Tool Standard Output
- Tool Standard Error
- For more information about specific tool errors, please see the Troubleshooting section
- Submit a bug report! If you are still unsure what the problem is.
- Click on the bug icon galaxy-bug
- Write down any information you think might help solve the problem
- See this FAQ on how to write good bug reports
- Click galaxy-bug Report button
- Ask for help!
- Where?
- In the GTN Matrix Channel
- In the Galaxy Matrix Channel
- Browse the Galaxy Help Forum to see if others have encountered the same problem before (or post your question).
- When asking for help, it is useful to share a link to your history